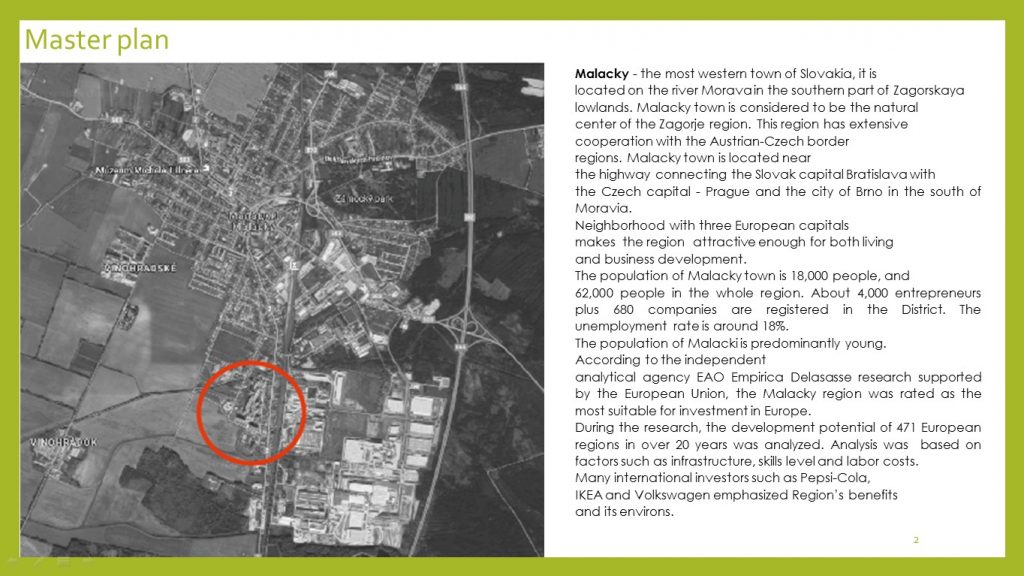
The project “Malacky – project proposals on improving the environment quality in Bethany center” aims to solve technical and social problems of staying at the Center by taking measures of improving the energy efficiency of the Center’s building, constructing a greenhouse, redesigning it and reassigning its premises to improve the comfort of the indoor environment as well as landscaping and greening its adjacent territories.

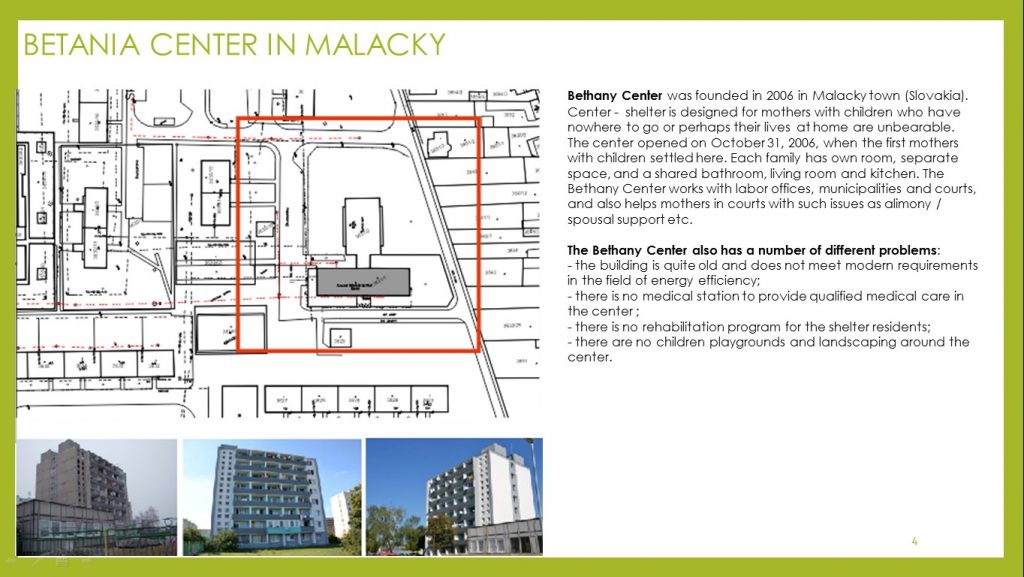
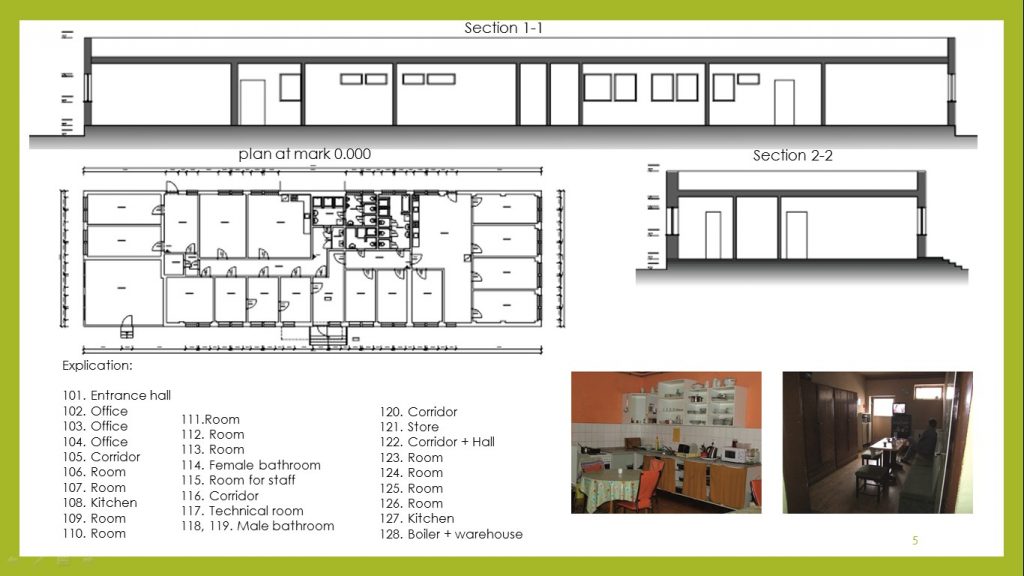
Center shelter Betania is designed for approximately 40 people. Each family is located in a separate room and has a shared bathroom, living room and kitchen.
There are a lot of different problems in Bethany Center:
– the building is quite old and does not meet modern requirements in the field of energy efficiency;
– in the center there is no medical station to provide of qualified medical care;
– there are no rehabilitation programs for the shelter residents;
– there are no children’s playgrounds and landscaping around the center.
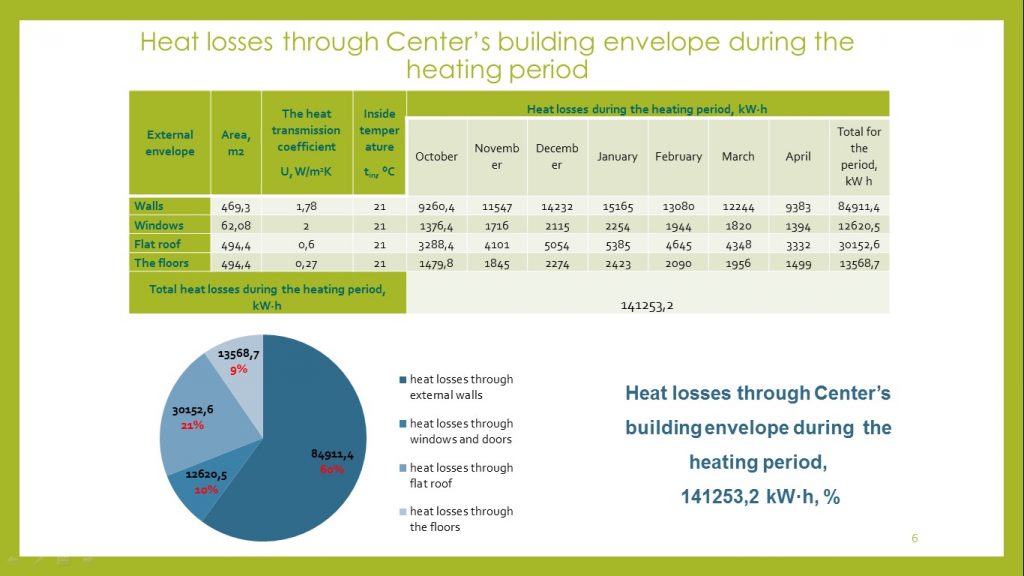
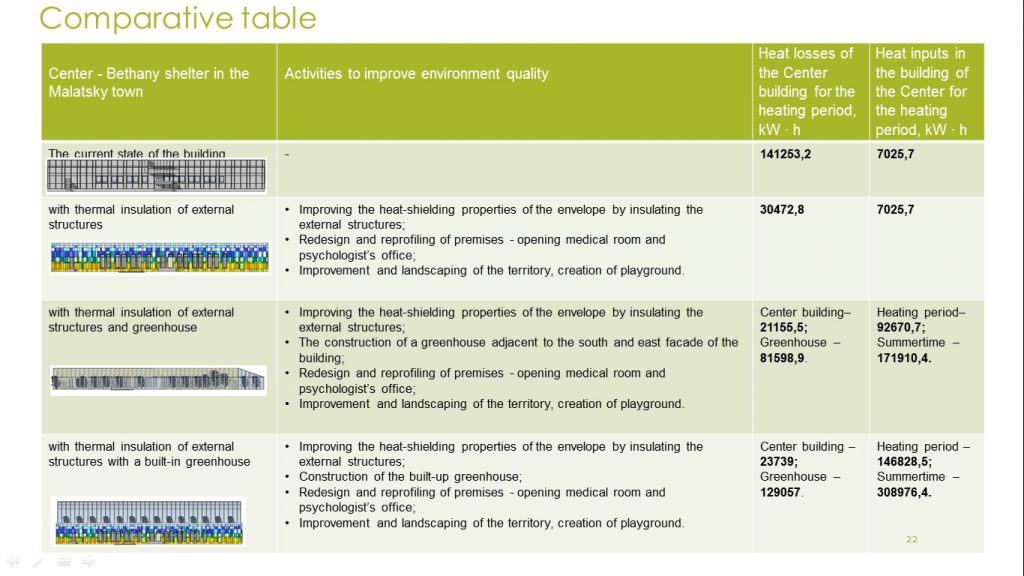
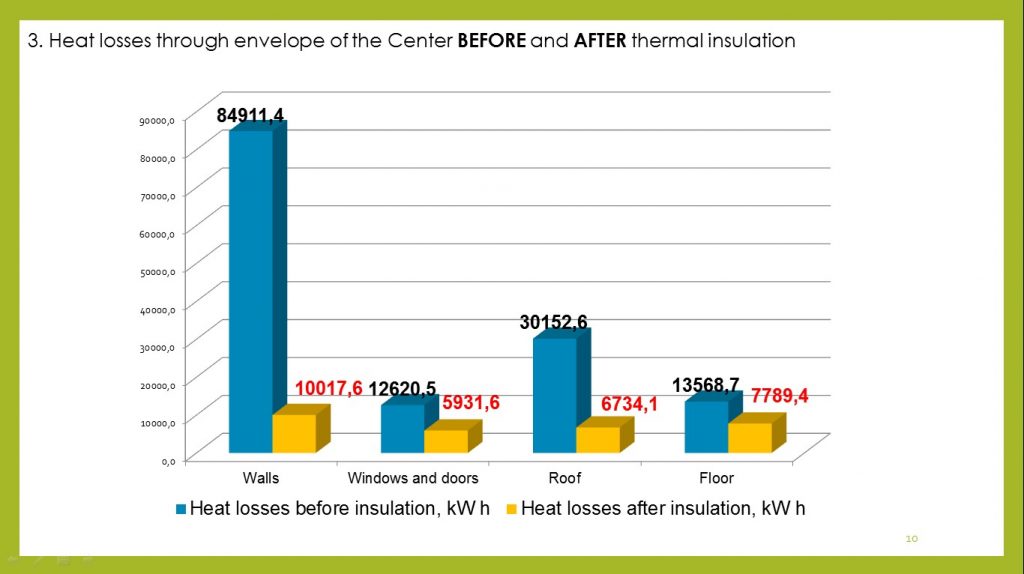
To develop measures aimed on improving the building energy efficiency and the microclimate quality of the Center’s premises, heat losses were calculated through the building envelopes monthly for the heating period.
The calculation results showed that the greatest heat losses occur through the external walls of the building – 60%, the smallest through the windows and the floors.
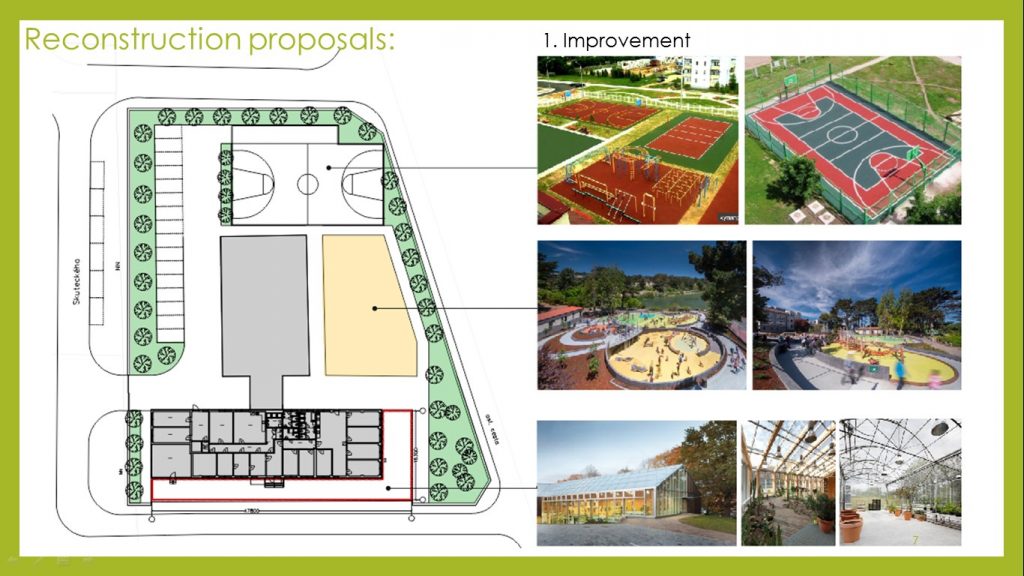
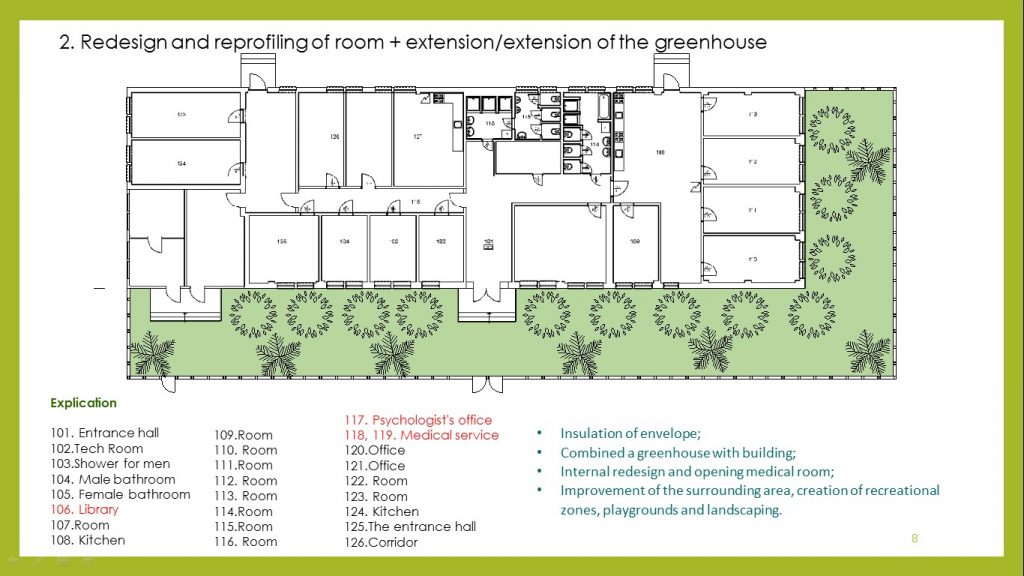
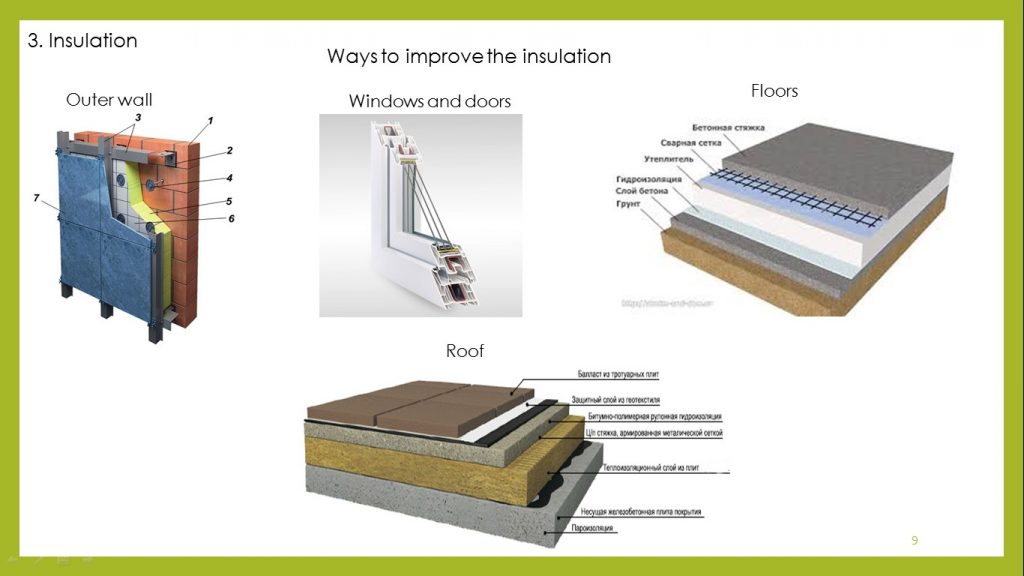
– improving the energy efficiency of the building, by thermal insulation of the external structures;
– construction of the greenhouse combined with the building of the Center;
– internal redesing and reprofiling of existing premises for the organization of a medical room;
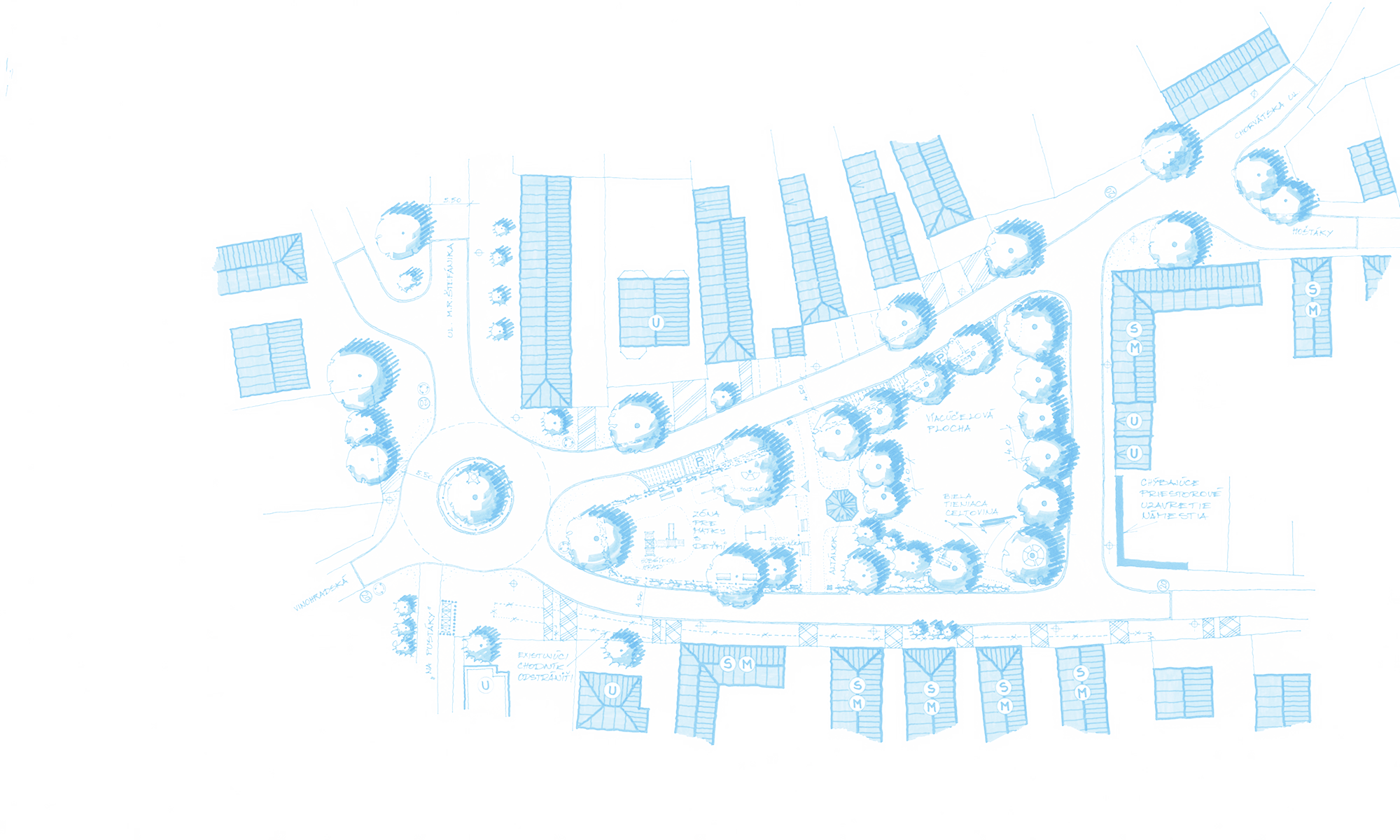
– improvement of the surrounding area creation of recreational zones, playground and landscaping.

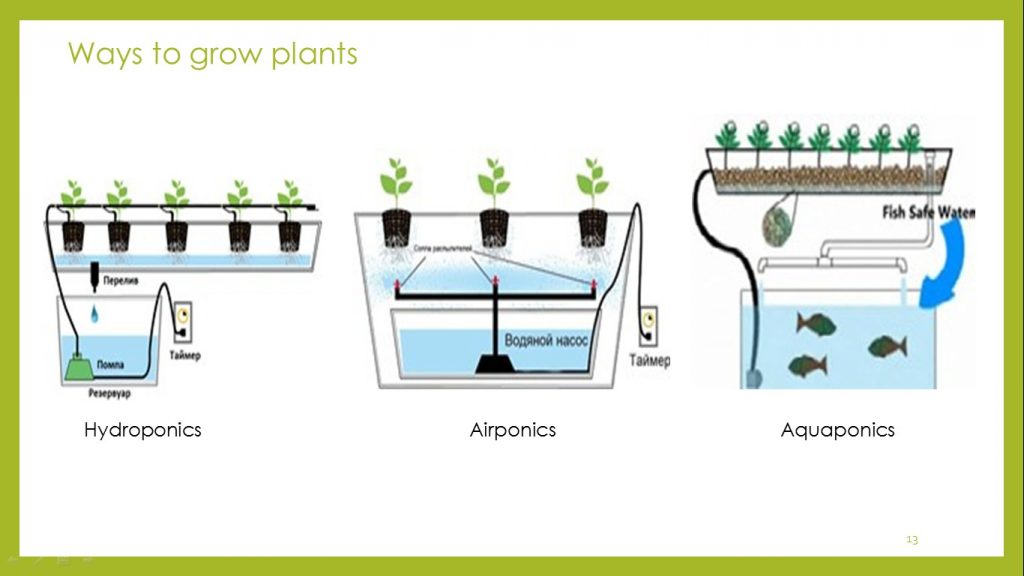
Gardening improves physical and mental health and decreases levels of the disease. London therapists even prescribe the time to patients for gardening.
In 2013, at Brockwell Park Surgery in South London,a food cooperative was established, where the unused space of hospital areas is reprofiled grooving areas into for patients. The soil has a beneficial effect on the brain. This effect is similar to the effect of antidepressants that improve the mood.

Greenhouses are used for growing vegetables, flowers, as well as for exhibition purposes (gardening shops, oranges, botanical gardens). For these various functions, different types of single or multi-level greenhouses of various sizes and shapes are offered.
The idea of growing plant products in cities, close to consumers, is becoming more popular. Ways to transfer this idea into reality are “Vertical Farms”, farms on the roofs of houses, underground farms.

Due to the transparent envelope of the greenhouse it is possible to accumulate most of the solar energy. Therefore, the greenhouse must be placed on the sunny side of the building, where insolation is provided mainly from February to November. The greenhouse functions as a solar energy storage device and contributes to the heating of the building and the reduction of heat loss.
In addition to the ventilation windows, ventilation openings can be placed in the upper part of the greenhouse to ensure communication with the cool side of the building.
For the arrangement of translucent covering of greenhouses it use such transparent materials: plastic slick, glass and polycarbonate.
To make a greenhouse frame it is possible to use materials such as wood or light-weight thin-walled steel structures.
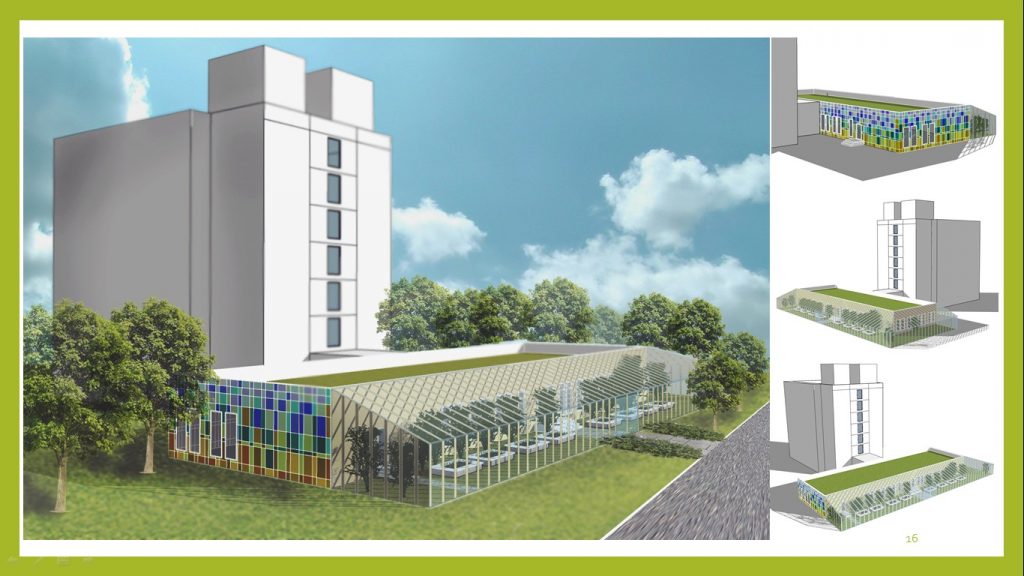
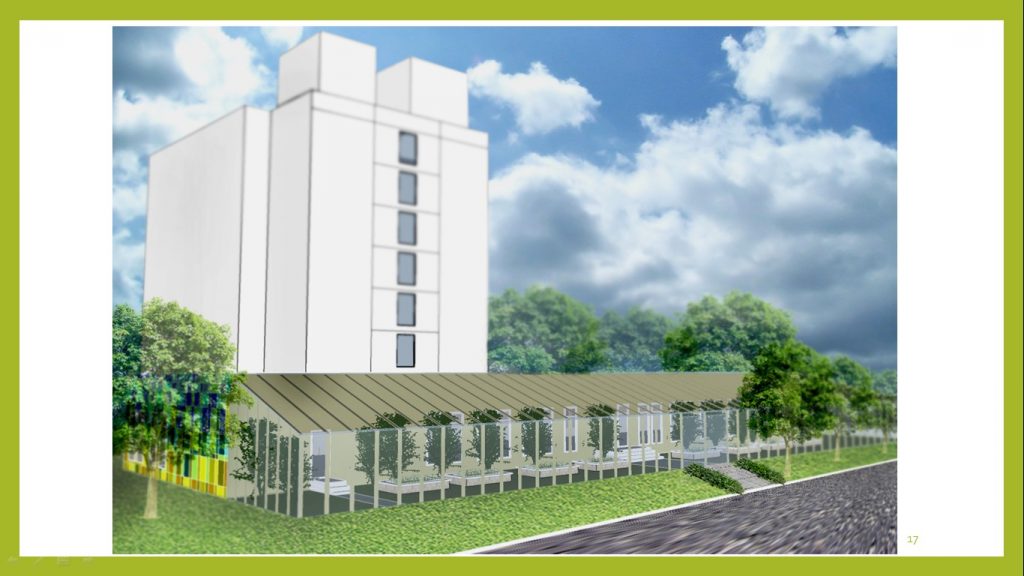
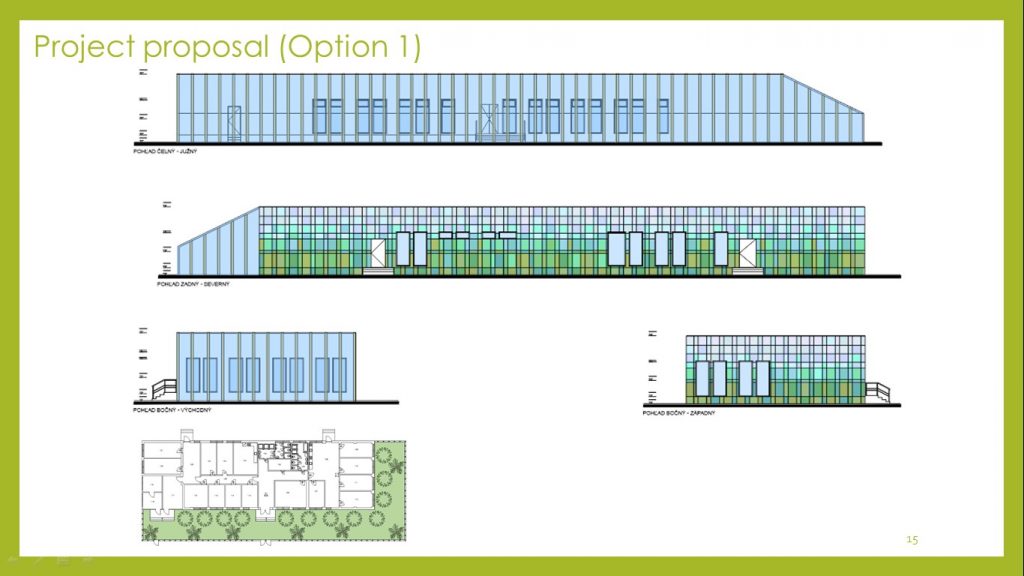


The first option is to construct a greenhouse adjacent to the building from the southern and eastern sides (as most favorable for the orientation of the greenhouse). The width of the greenhouse is accepted – 5 m. The length of the greenhouse is taken according to the length of the building. Greenhouse height up to 4.5 m – to the height of the building.
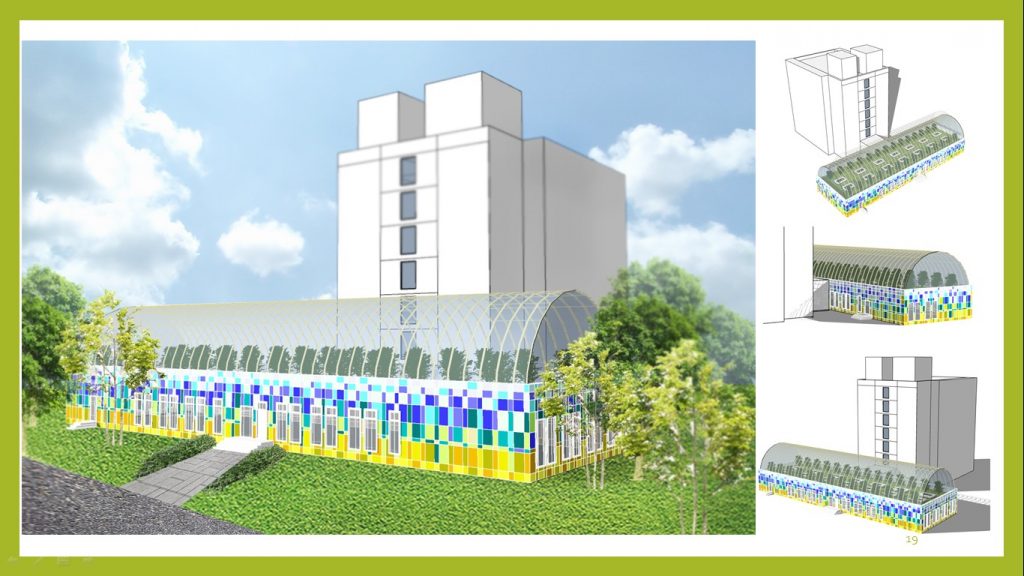


The second variant involves the construction of a greenhouse on the roof of the Bethany Center building. It should be noted that such option is possible only with sufficient bearing capacity of the existing building structures.
For the construction of greenhouses in the center of Bethany, we propose to use a frame made of light steel thin-walled structures. As a material of translucent covering in the greenhouse we use cellular polycarbonate, 16 mm of thickness.
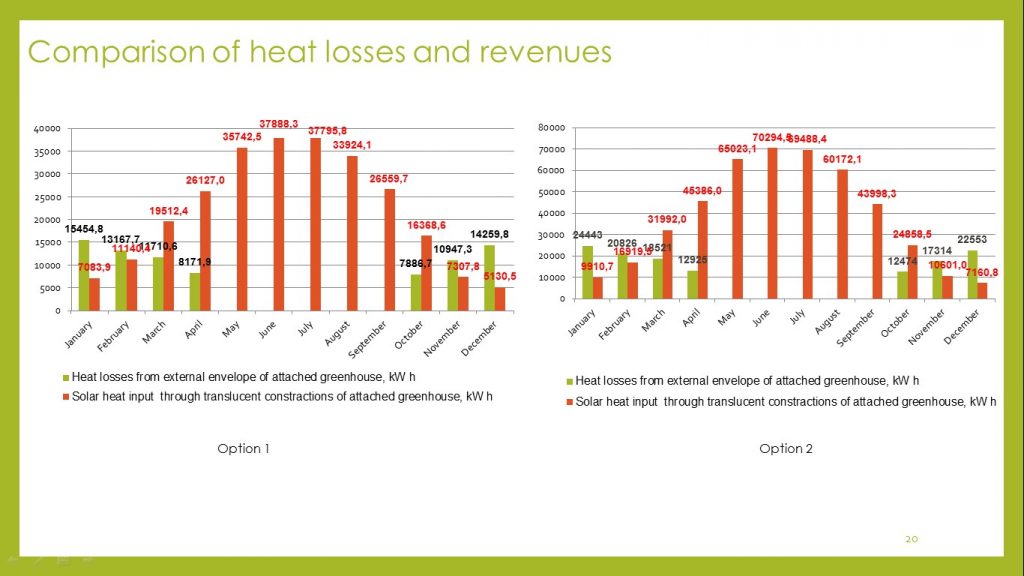
In both cases, the annual heat inputs significantly exceed the annual heat loss of the building. But at the same time, due to the climatic conditions, heat inputs are unevenly distributed throughout the year during the coldest winter months (November, December, January, February) and heat losses significantly exceed heat inputs.
Therefore, we can conclude that for the greenhouse exploitation for whole year it is necessary to provide additional sources of heating during the coldest period or means of external protection of translucent structures from overcooling (external louvers).
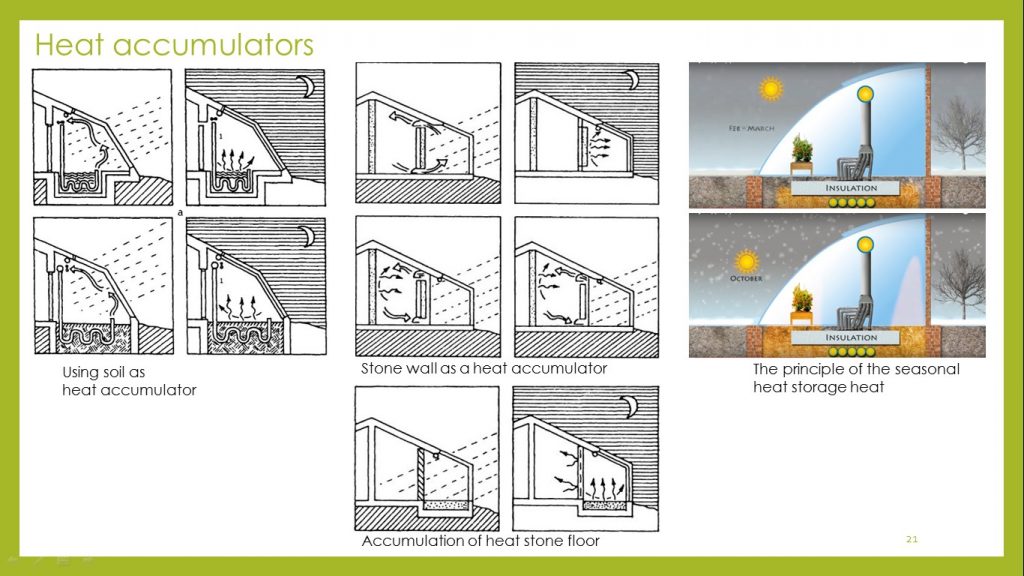
As heat accumulators in a greenhouse could be used: elements of its structure (floor, walls, soil) and individual objects installed in it (containers with water, stones).